Analysis of the relationship between design thinking and brain activity using the NIRS and eye-tracker apparatuses
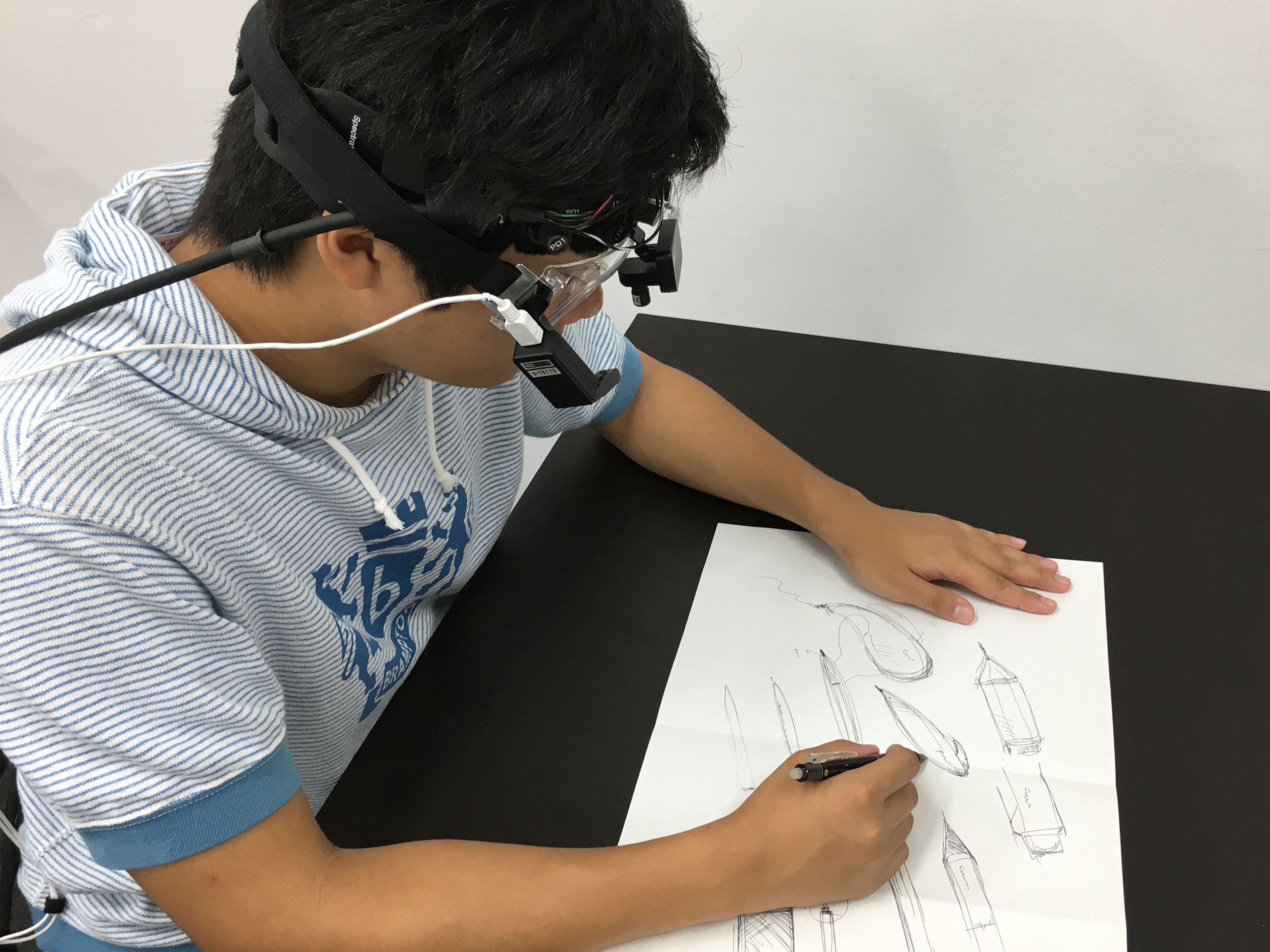

Design thinking is a process that helps designer’s problem solving in design activities. Our laboratory aims to quantify the brain activity during the design thinking activities, using the near infrared spectroscopy (NIRS) and eye-tracker apparatuses. For example, our laboratory measures and analyzes the brain activity while a subject draws sketches for designing, which is a representative idea generating method employed during design thinking.
Modularization of the product parts using design structure matrix
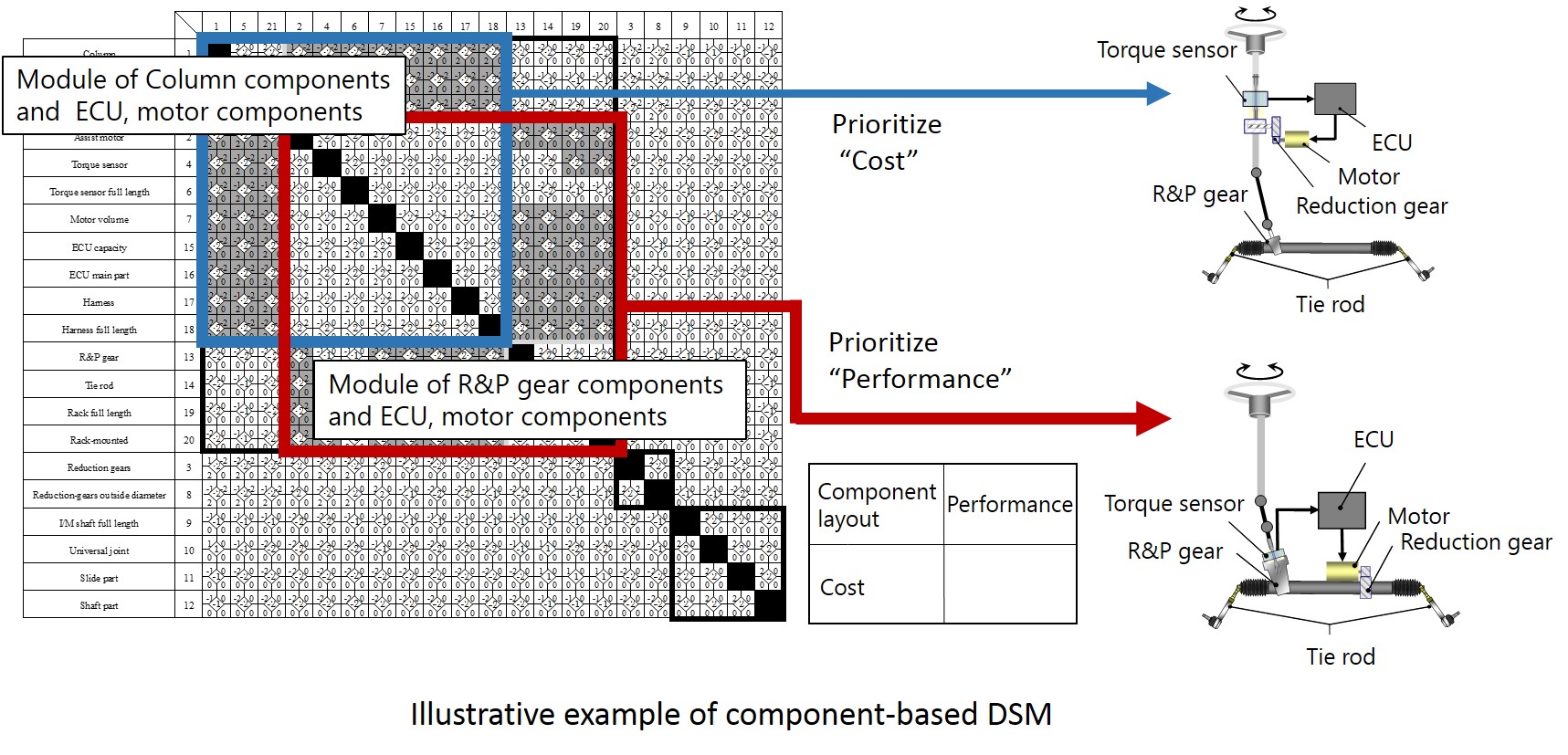
Design structure matrix (DSM) is a matrix to organize the various topics related to the product design (e.g. the components and functions of the products and the development team and process). Our laboratory focuses on the Component-based DSM to organize the product components. We work on constructing a method to modularize the product components when there are the trade-off relationships between some characteristics (e.g. energy input and output, components arrangement, and cost) which define the relationships between the product components.
Analysis of the relationship between Kando(emotion) and brain activity using the NIRS apparatus
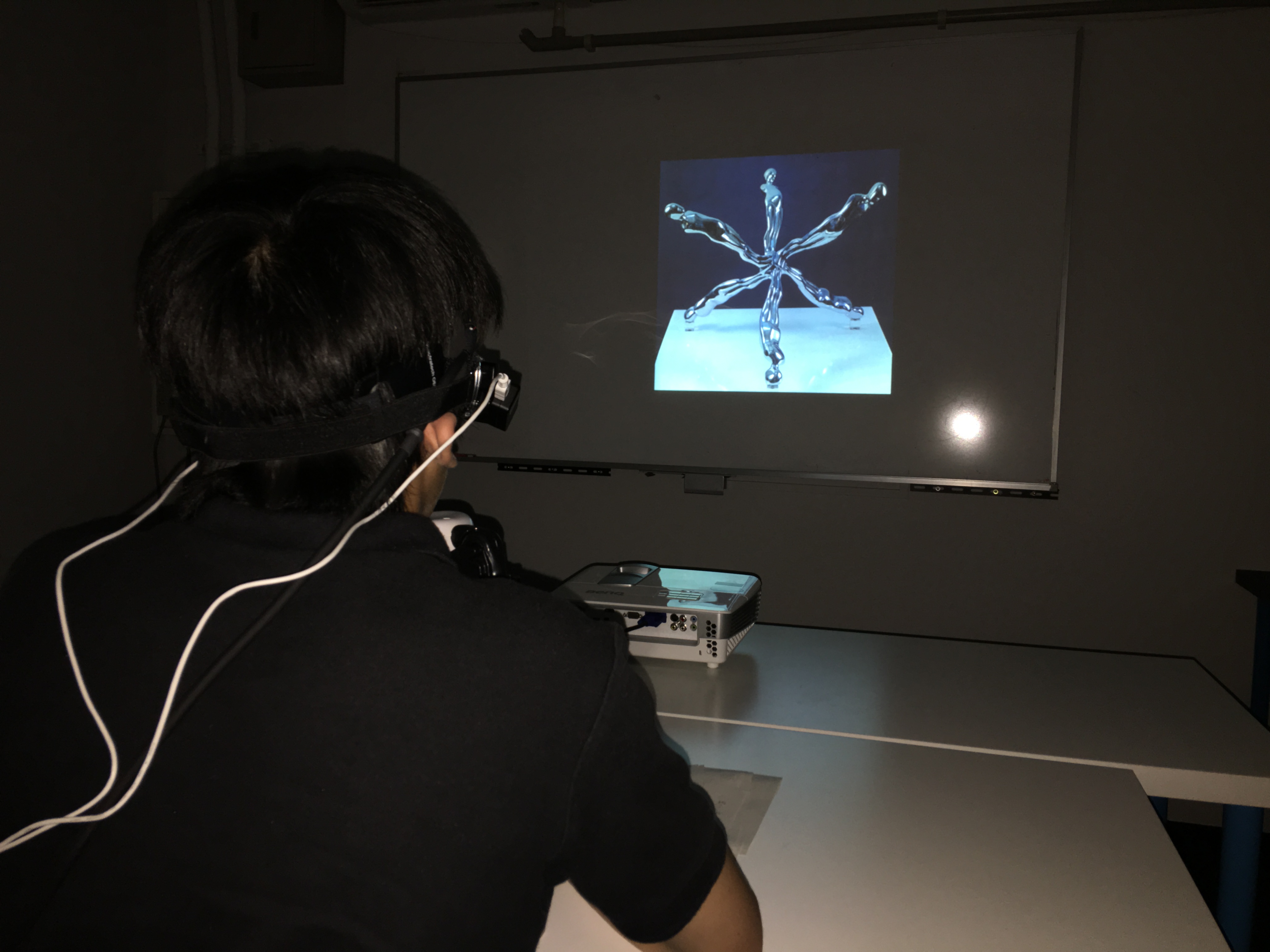

The customers’ requirement has been changing from the artifact satisfaction to the mental satisfaction. Therefore, the physiological index to objectively evaluate Kando(emotion) is required. Our laboratory aims to quantify the brain activity while Kando arises using the near infrared spectroscopy (NIRS) apparatus to measure the cerebral blood flow. We measure and analyze the brain activity of the subjects appreciating the works of art.
Value growth design for mobility system
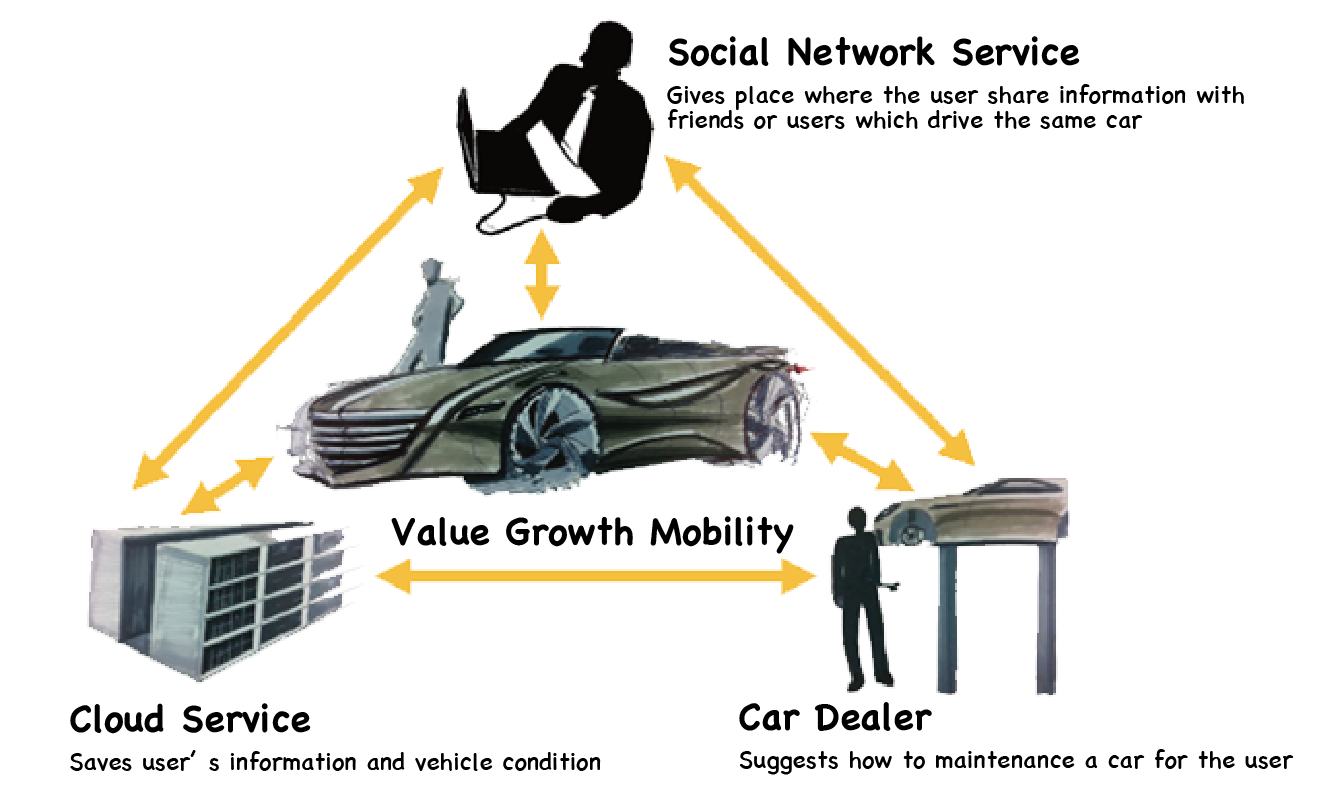
Value growth design is a design concept to improve the product value as the time passes. This prolongs the use period of the products and has the potential to change the mass production and mass consumption society. Our laboratory surveys and analyzes the value growth cases of automobiles, including the driving technique improvement support system, which gives the drivers to the growth of the values such as trust and relief.
Improvement of set-based design using metaheuristics
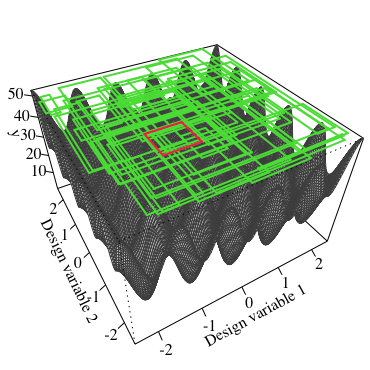
Set-based design method derives the range of the design variables that fulfil the preferred range of performance. This method can reduce the effect due to the design changes. Our laboratory works on improving the calculation efficiency to derive the range of design variables using metaheuristics such as genetic algorithm (GA) and particle swarm optimization (PSO). Moreover, we work on improving this method by assuming the uncertainties in product design as in processing errors and use environments.
Model-based conceptual design method
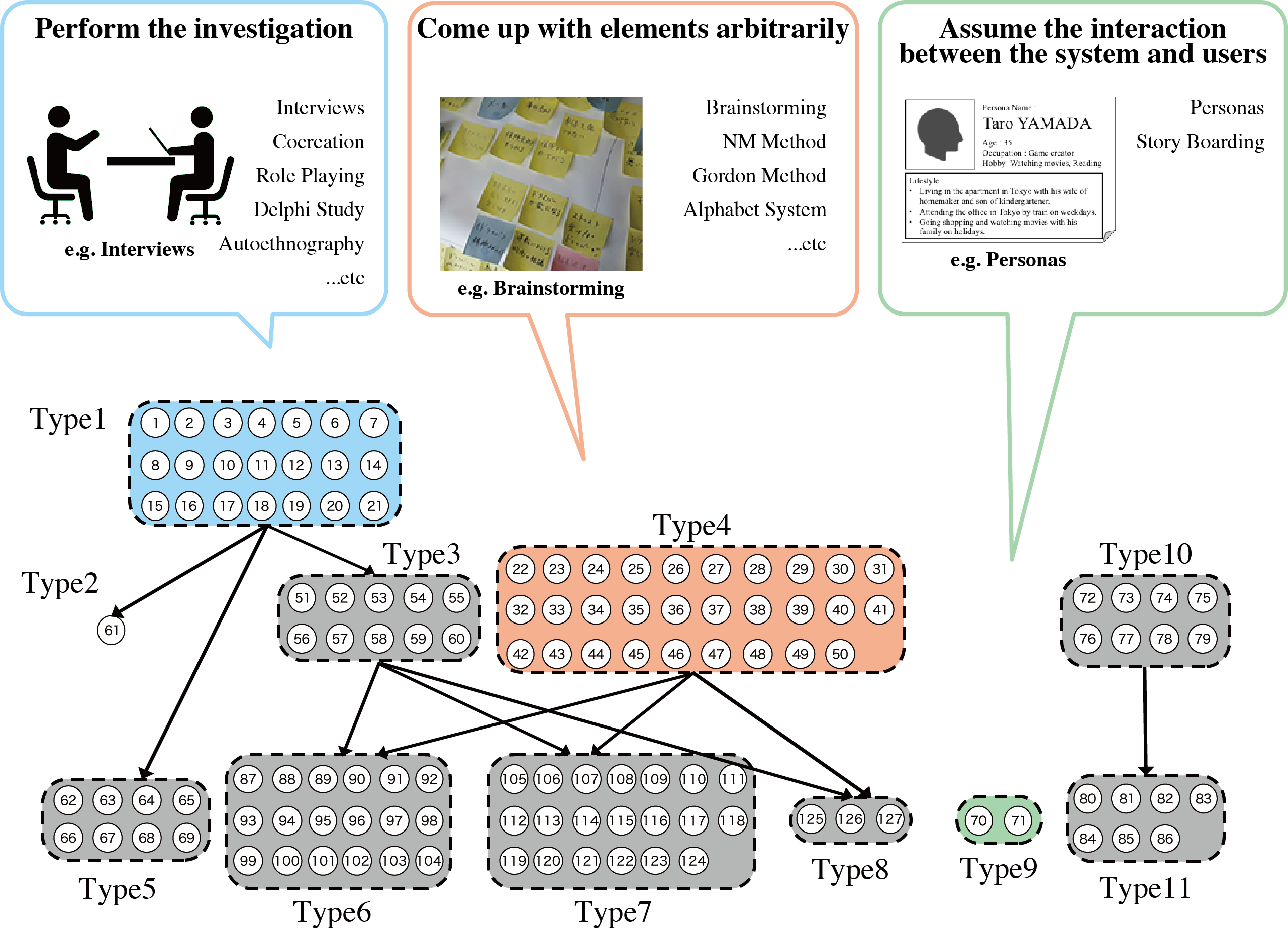
Model-based systems engineering is an approach for systems engineering, which represents the products information (e.g. formulas and sentences), using diagrams. Although, the model-based systems engineering lacks the models to represent information in the conceptual design stage of a product development. Our laboratory works on constructing the valid method for the conceptual design, by analyzing the characteristics of the conventional design methods.
Quantification of Human Emotion Using NIRS
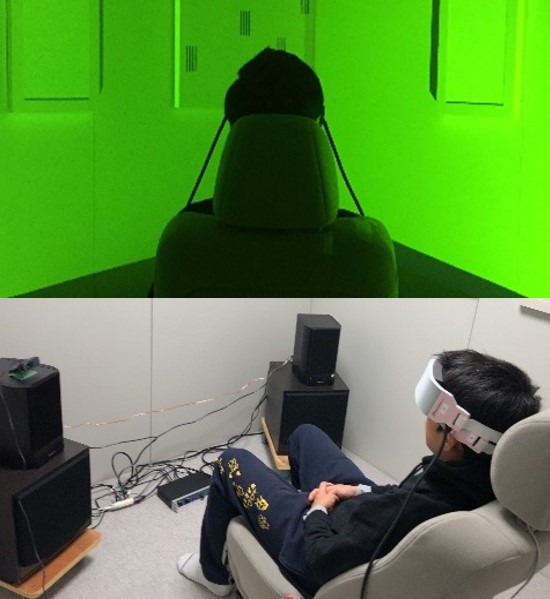

Human emotion is subjectively evaluated by sensory evaluation experiments in most cases. This study utilizes NIRS (near infrared spectroscopy) apparatus and aims to clarify the relationship between the sensory evaluation and brain activities. For example, we measure the brain activities of the participants staying in the different colored illumination and analyze the correlation between the measurement results and the sensory evaluation values regarding comfort, arousal, and so forth.
Curved surface shape generation method based on emotional evaluation about shapes
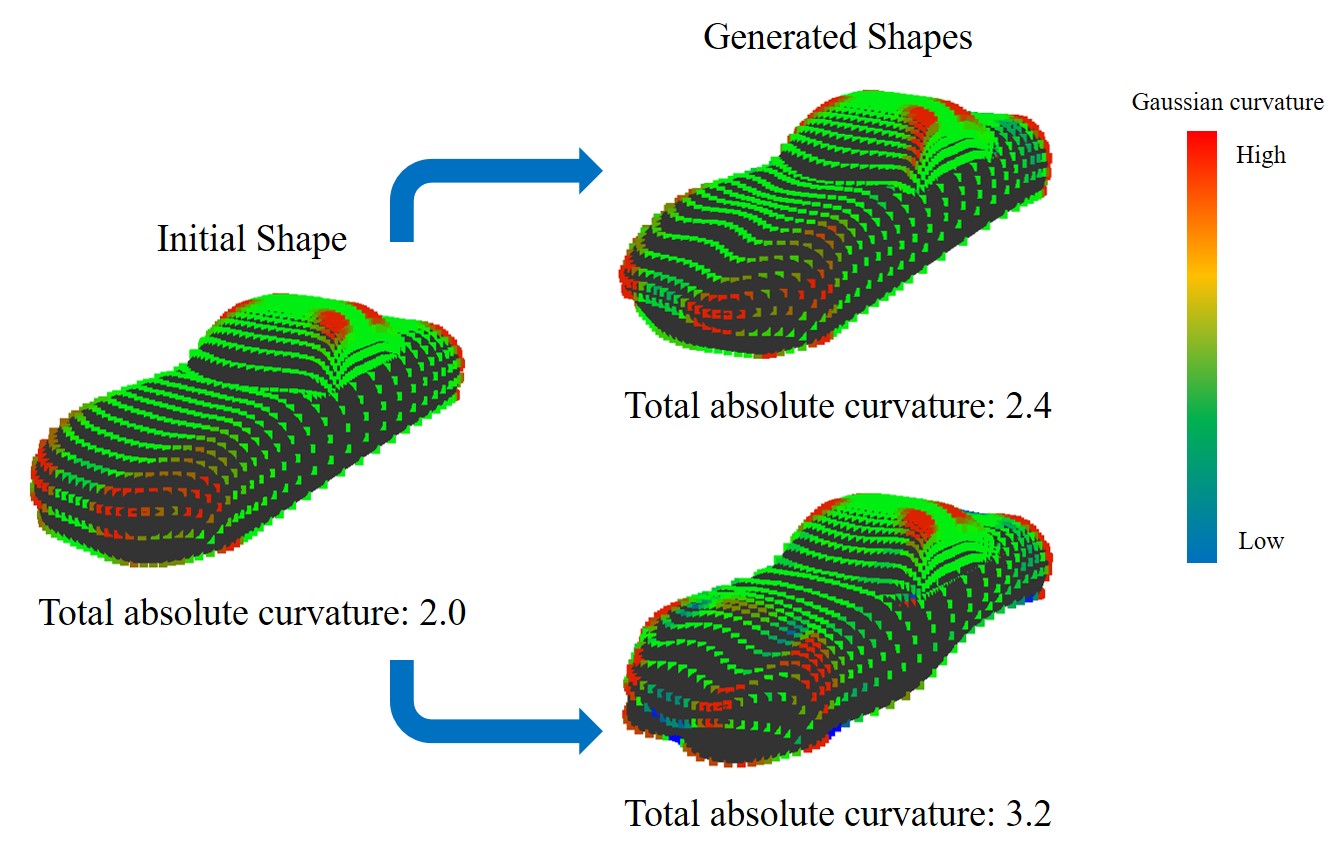
In recent years, Generative design, in which computers generate the shape of industrial products has attracted attention. However, most systems generate the shape based only on the engineering (mechanical) evaluation and require to include the emotional evaluation of human in order to apply to industrial design field. Our laboratory works on the construction of a system which automatically generates curved surface shapes based on the proposed indices of shape features: “total absolute curvature” and “Gaussian curvature entropy”.
Generation of 3D voxel shapes using machine learning
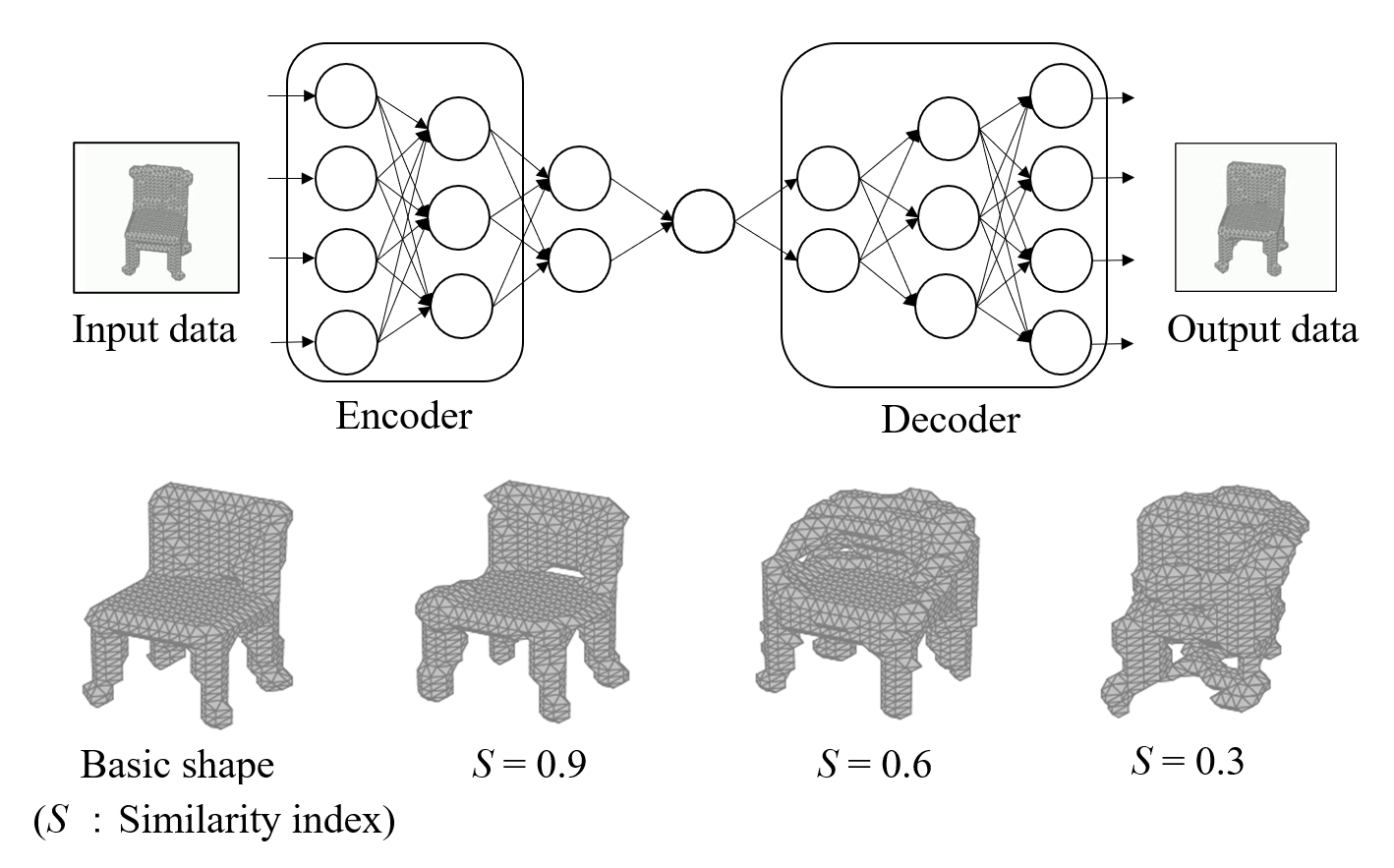
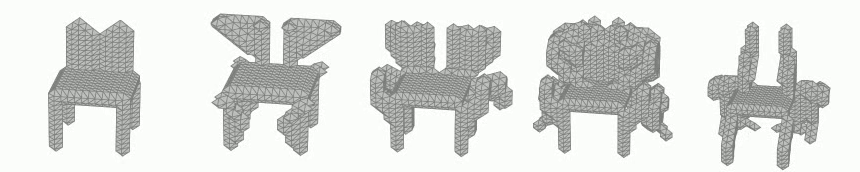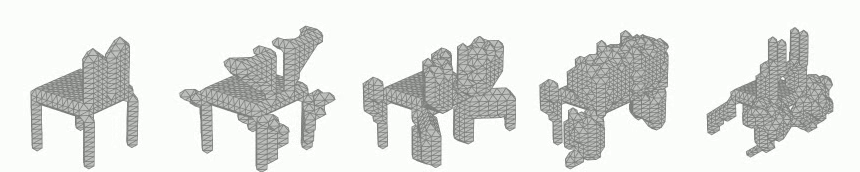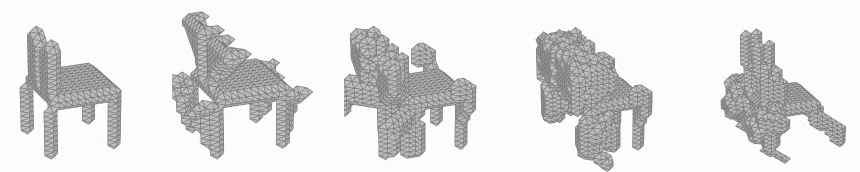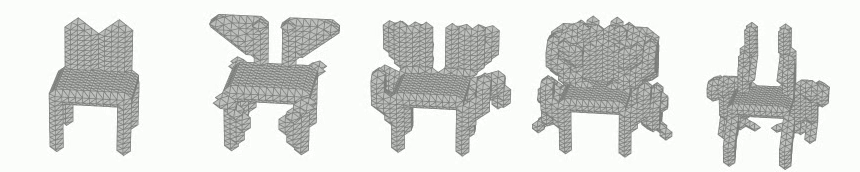
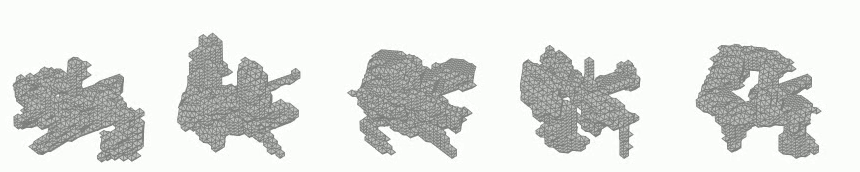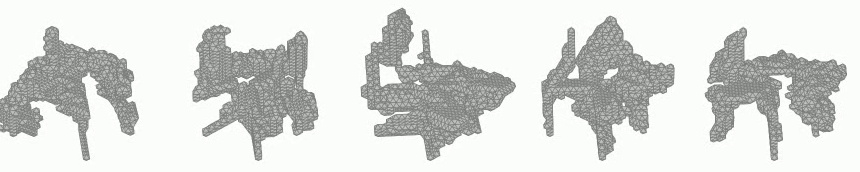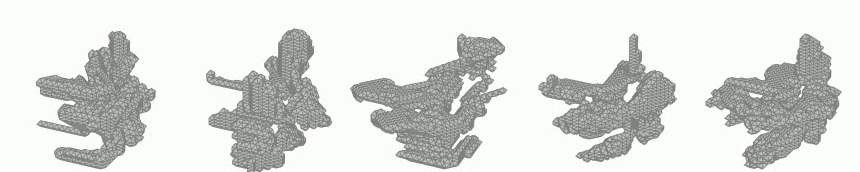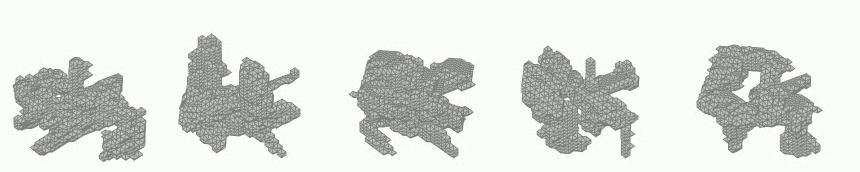
In recent years, computational aesthetics that infer the user’s aesthetic preference from morphological information have attracted attention. This study aims to quantify the aesthetic preference for three-dimensional shapes by using the similarity index between shapes obtained by a machine learning: VAE (Variational Autoencoder). In addition, we are working on the construction of a system that generates 3D voxel shapes based on quantified aesthetic preferences in order to support designers’ ideation.
Sharing Economy
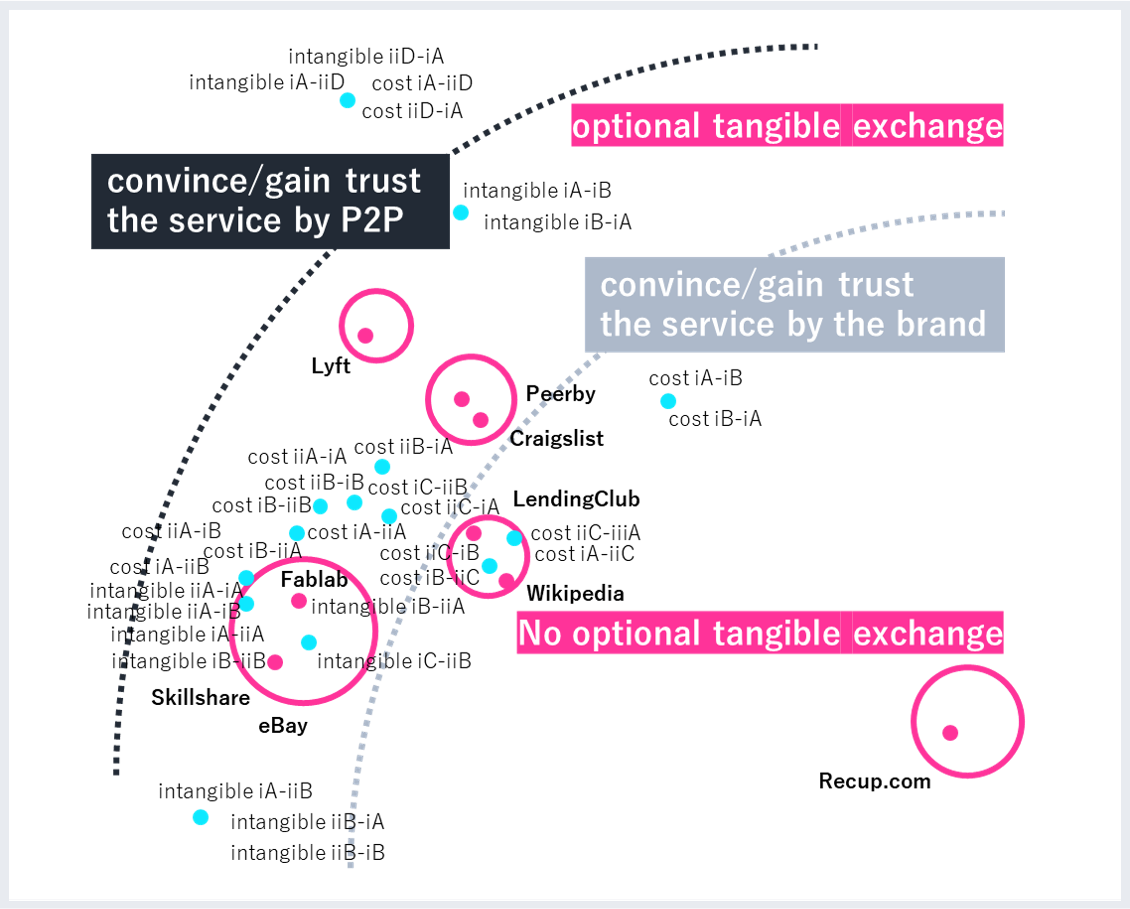
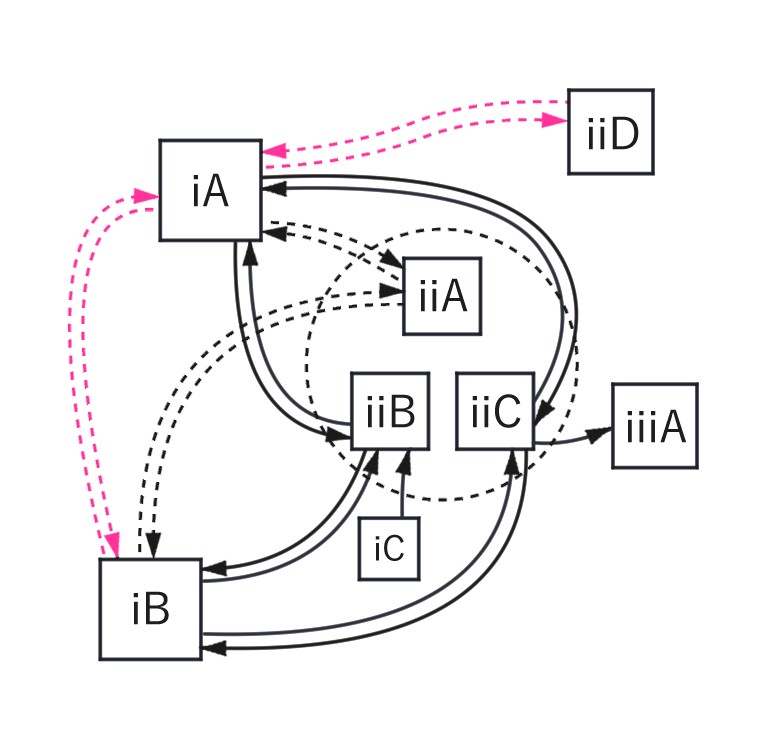
“Sharing Economy” has been attracting a lot of attention as an economic activity/service in which products and service are shared among the stakeholders. However, the standards and design methods for such services have not been established. This study aims to propose the design method/guidelines by adding 1) the mental models of peers; 2) the analysis of “trust” between peers; 3) the viewpoint of the difference of sharing services between countries.
???
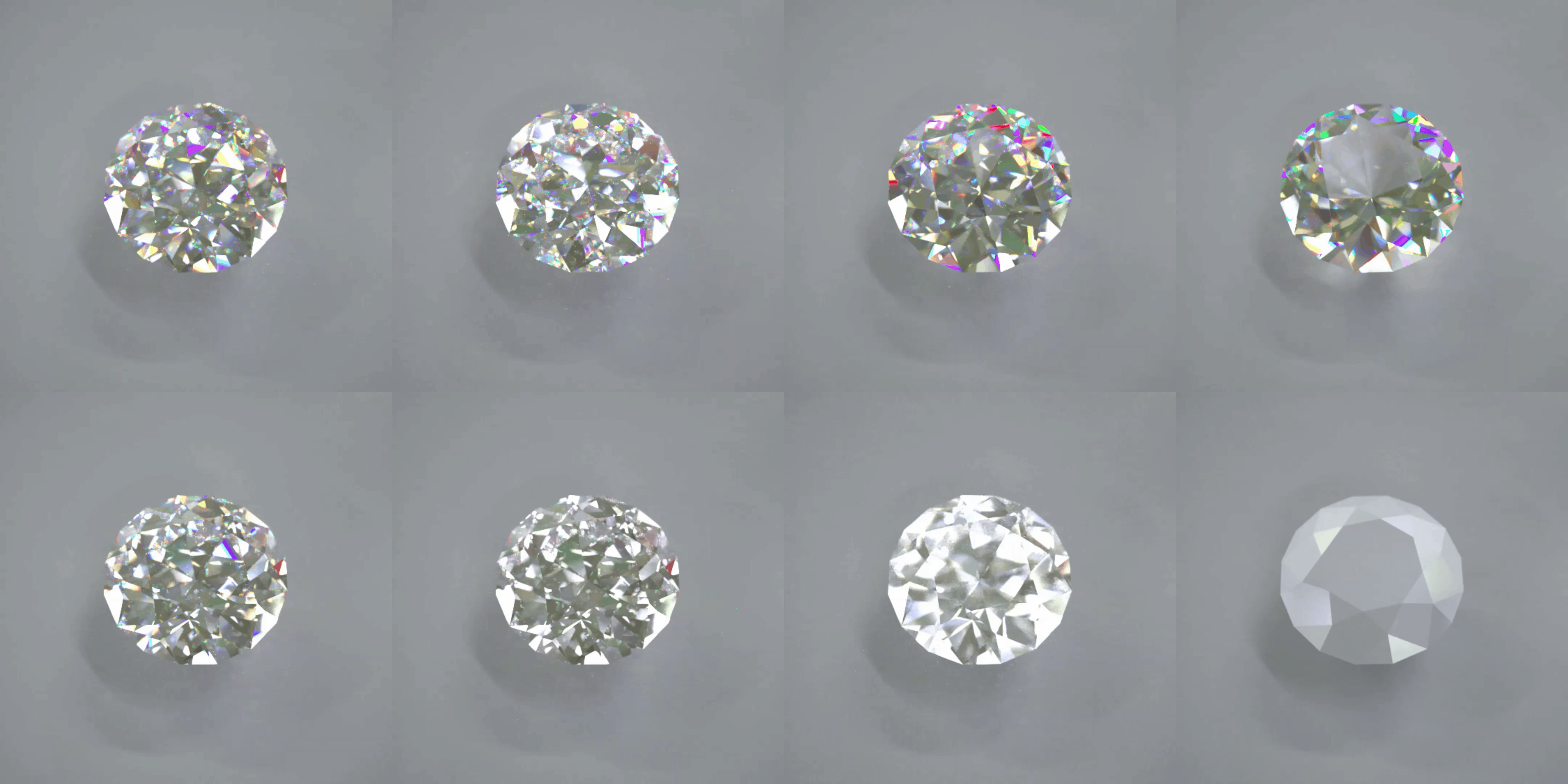

Recently, the market has placed emphasis not only on the functional value of a product, but also on its emotional value. And the design evaluation of products has become one of the most important processes in product development. We analyze the effects of optical characteristics and image features on human aesthetic preferences using optical simulation and image analysis techniques. For example, we analyze the relationship between human aesthetic preferences for diamond sparkle using optical simulation diamond videos with various optical properties.
Cross-modal effect between taste and shape controlled by curvature entropy
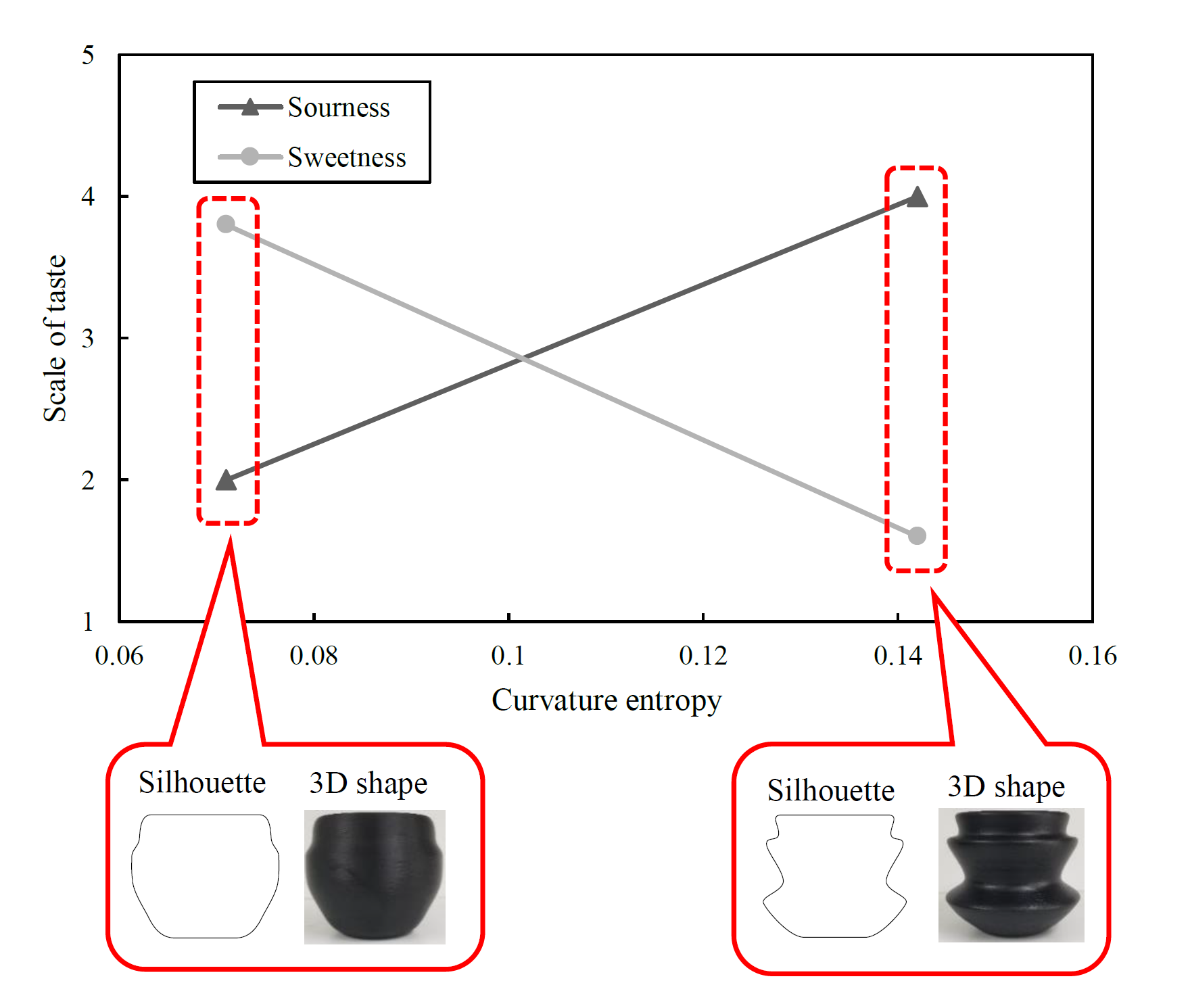
In recent years, cross-modal effects in which perceptions interact with each other have been drawing attention. Previous studies have shown the cross-modal effect between vision and taste that an angular shape enhances sourness and bitterness. However, the characteristics of shape samples used in those analyses have been evaluated qualitatively, and no quantitative study has been conducted. Therefore, this study aims to clarify the cross-modal effects using curvature entropy, a quantitative index of “complexity” related to shape.
Non-contact musculoskeletal load estimation system using infrared depth camera
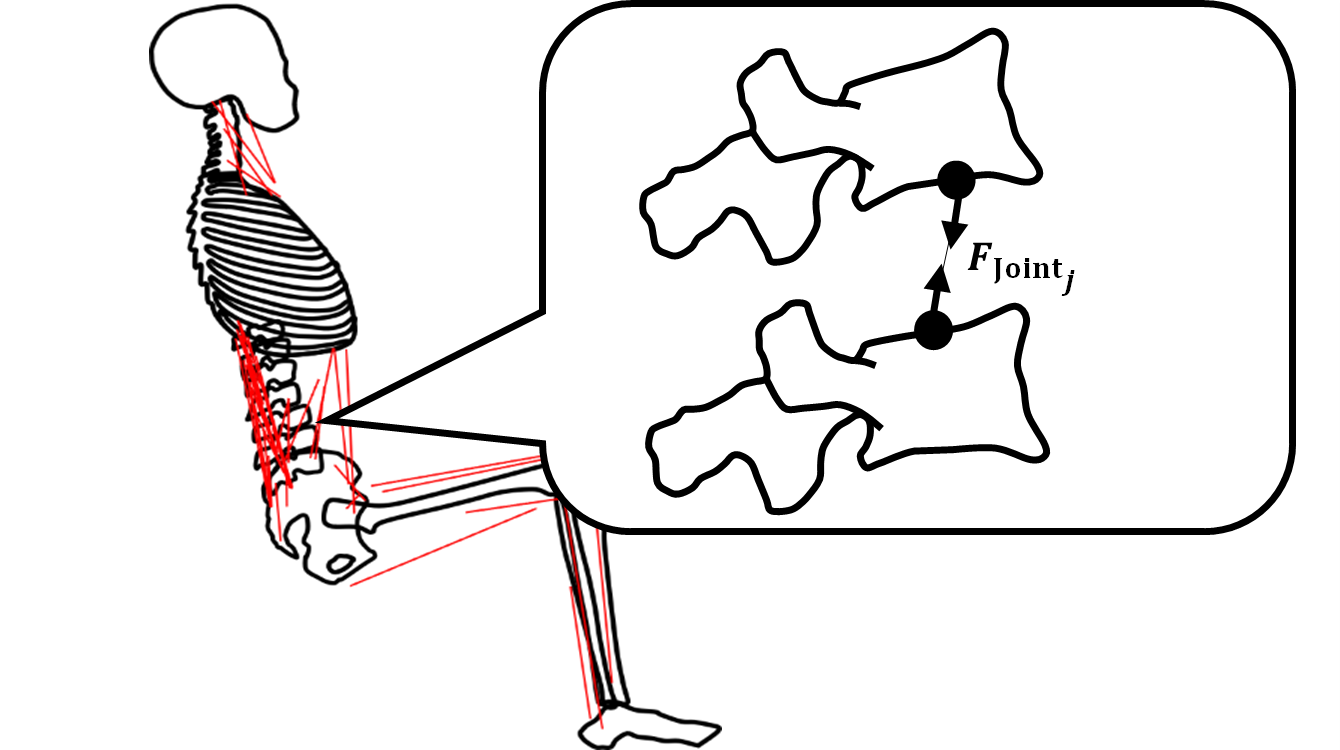
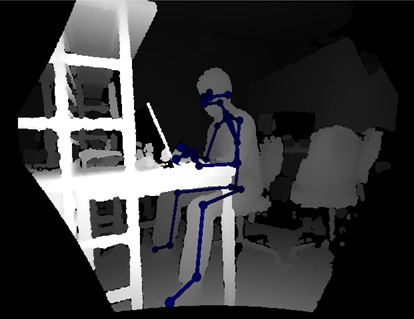
The remote work has become common and causes the difficulty to ensure the health during working hours in ill-equipped residential environments. This research develops a system to estimate the loads on the body, such as joint compression force and muscle stress, when s/he takes a seating posture for VDT work by using an infrared depth camera.